
We’ve compiled a list of recalls issued by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and US Department of Agriculture (USDA) from this past week:

We’ve compiled a list of recalls issued by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and US Department of Agriculture (USDA) from this past week:

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.

Roughly half of all American expectant mothers living with HIV are receiving treatments that don’t meet federal guidelines. A new study examines prescribing choices for this population.

A new study provides detailed description of newly identified BoDV-1 induced encephalitis cases, establishing the infection as a potentially lethal zoonosis which can impact immunocompromised and healthy individuals.
A closer look at the 2018 enterovirus A71 outbreak in Colorado highlights the need for non-sterile site testing to detect infections.

As of January 5, 2020 there have been 59 confirmed cases associated with the pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan city.

The FDA has approved a supplemental new drug application for micafungin for the treatment of invasive candidiasis in pediatric patients under 4 months of age.

A new study found that the estimated time from HIV seroconversion to initiation of ART was reduced by 42% between 2006 and 2015 in New York City.

Some asymptomatic carriers of C diff went on to have clinical infection themselves within a 6-month period.
A new retrospective cohort study has confirmed that rates of hospitalization for serious infections among people with substance use disorders are increasing, particularly among young people.
New findings provide insight on the mechanisms of malarial resistance, demonstrating that inactivation or mutation of Kelch13 compartment proteins reduces the parasite’s uptake of hemoglobin.
Results of a study published in Pediatrics found that 8 of 10 children with a non–β-lactam antibiotic allergy could be delabeled.

A study in JAMA Pediatrics suggests that infants exposed to Zika in utero who do not show signs of congenital Zika syndrome may still be at risk for abnormal neurodevelopmental outcomes.
A new article in Open Forum Infectious Diseases outlines practical strategies for treating opioid use disorder in the context of associated infectious diseases.

A new study is shedding light on how bioburden and patient colonization play off each other.

Viral suppression at 2 years nearly doubled for people with HIV in a medical care coordination program implemented by the Los Angeles County Division of HIV and STD Programs, a new study found.

Earlier initiation of DAP-CPT combination therapy may be beneficial, despite a tendency to use the therapy after initial treatment failure.

In a head-to-head comparison, investigators found that 3 enhanced flu vaccines provided better protection for elderly patients compared to standard-dose vaccines.
Women and adults aged 65 or older were particularly affected by the increased incidence of nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease infections.

We are taking a look back at the top articles published in Contagion®’s print journal in 2019.

Here is a look at infectious disease-related US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) news from the week of December 29, 2019.

We’ve compiled a list of recalls issued by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and US Department of Agriculture (USDA) from this past week:

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.
Treating parents colonized with S aureus reduced neonatal colonization with concordant S aureus strains when compared to placebo.
According to a new report issued by the WHO, the global incidence of cholera cases decreased by 60% in 2018.
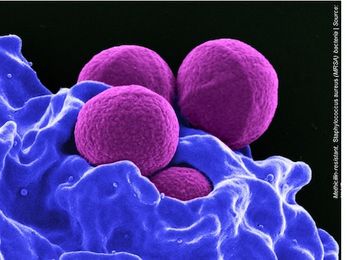
A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation may offer some insight on why past efforts to develop a vaccine for S aureus have failed.

The Bacille Calmette-Geurin vaccine is typically administered intradermally, which may not generate enough T cells to elicit strong immune responses in the lungs to effectively protect against TB.

Exploring the antibiotic commercial conundrum. ​

The CDC MMWR provides a summary of the Ebola response from August 2018 to November 2019, noting 2196 deaths and consistent challenges in outbreak control due to government mistrust and ongoing armed conflict.

Investigators of a new, multisite study evaluating neuropsychological development in African school-age kids found that children with perinatally-acquired HIV had poorer results on neuropsychological tests despite early ART initiation and viral suppression.