
Zoonotic & Vector-Borne Diseases
Latest News
CME Content




Research coming in from Fernandes Figueira-Fundação Oswaldo Cruz finds that when it comes to diagnosing Zika virus infection in newborns, the eyes may have it.

Although the yellow fever outbreak that has affected several Latin American countries has eased since the end of summer, health officials say new cases are still springing up in some areas.

Researchers from the Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene have found that pet owners are at increased risk of encountering ticks.
The CDC offers further insight into the investigation of a Zika virus infection in a family member of the first Zika-related death in the continental United States.

The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is looking to determine whether Zika virus infection poses an additional risk in women whose pregnancies are already complicated by HIV.

Researchers from EcoHealth Alliance have developed a predictive “map” that identifies the zoonotic host species that are “likely to harbor the next human virus” and documents the regions of the world where they can be found.

A look into how health information exchange interventions are beneficial in HIV care; the discovery of 3 mutations that could help the bird flu spread among humans; news about a new patch formulation for the flu vaccine; progress towards an HIV vaccine; and information on an interactive map that visualizes the US HIV epidemic, make up the Top 5 articles for this week.

New HPV vaccine recommendations from the World Health Organization, information on a new once-daily treatment for HIV, the potential underestimation of tick-borne diseases in the Western United States, norovirus outbreaks in California schools, and how reservoirs of latent HIV hinder the quest for a cure, make up the Top 5 articles for the month of June 2017.
As Colorado reports its first human West Nile virus case of the season and California reports its third, health officials around the country are emphasizing the importance of mosquito control and prevention.

Scientists have identified 3 mutations that could allow the avian influenza strain H7N9 to spread among humans.

Measles in Ontario, more endoscope-related infections, a study of postnatal Zika infections, research and development on a river blindness vaccine, and using CRISPR to tackle Zika are the articles that make up this week’s Top 5.

Drought-stricken not long ago, California is now dealing with flooding waterways, raising concerns that the water will create breeding grounds for West Nile-positive mosquitoes.

A team of researchers from several institutions have received a grant to fund the development of a vaccine for onchocerciasis, the second leading infectious cause of blindness.

Can genetic modification aid us in fighting mosquito-borne diseases?
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) has partnered up with nonprofit foundation FUNSALUD to launch a study that will examine the effects of Zika infection in infants and children living in Guatemala.
As researchers discover Chikungunya-carrying mosquitoes in Brazil, a new study analyzes the impact of the Zika virus on the area.

Although treatment for chronic Lyme has provided some patients with relief of their symptoms, it may also expose them to complications related to the prescribed modalities.
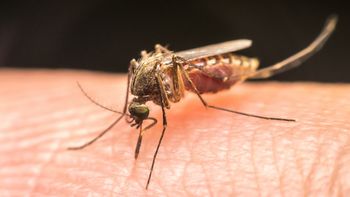
The CDC just released a study outlining areas where an increase of Aedes mosquitoes was observed in 2016. In addition, researchers report on Zika-related complications observed in 7 infants, postmortem.

Health officials in New York City are seeing the first West Nile virus-positive mosquitoes of the season as Los Angeles County reports its first human case of the year, marking new West Nile activity in the country’s biggest urban areas.

New drugs for HIV, the growing rate of antibiotic resistance, a new hepatitis C treatment option, and updates on the Ebola outbreak and Lyme disease diagnostics, make up the Top 5 articles for this week.

Two adults were hospitalized in Maine as a result of Powassan virus encephalitis.

Amesh A. Adalja, MD, FIDSA argues that a bill being considered in the Pennsylvania state legislature will ultimately result in increased antibiotic resistance and will set back the clock for finding appropriate treatments for Lyme disease.

































































































































