William Perlman, PhD, CMPP
Articles by William Perlman, PhD, CMPP

By targeting CabA, an extracellular matrix protein essential for biofilm formation, it may be possible to reduce the incidence of food-borne illnesses caused by the potentially lethal Vibrio vulnificus marine bacterium found in biofilms on oyster shells and meat.

Based on 2D and 3D in vitro models, treatment with mycophenolic acid confers very high levels of drug resistant rotavirus viral replication suppression and may therefore be a useful immunosuppressive agent for preventing rotavirus infection in transplantation patients.

Individuals who handle foods in the course of their work, as well as those working in healthcare settings, have a higher risk for infection with highly contagious, gastroenteritis-inducing noroviruses when an outbreak occurs where they work.
A new model of the within-host evolutionary arms race between viral pathogens and the adaptive immune responses intended to fight them suggests that vaccines based on genetically diverse sets of viral antigens may be more likely to stimulate the production of antibodies capable of neutralizing broad panels of virions.

Although several ambitious initiatives intended to put an end to the AIDS epidemic have been developed and implemented, this laudable goal will be difficult to achieve without substantial and wide-scale changes in HIV prevention strategies.
Additional study findings indicated that patients with AD had a significantly higher risk for S. aureus colonization of lesional skin as compared with those without AD.

In HIV controllers, both T follicular helper (TFH) and non-TFH lymph node CD4 T cells contain HIV.
Following an outbreak of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) identified at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora over three months in 2014, a potential association has been found between enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) infection and AFM in pediatric patients.

Those patients who survive infections caused by the Ebola or Marburg viruses may gain at least partial immunity to other filoviruses through specific antibodies generated during serological immune responses.

The belief that patients may face increased risks of complications following reduced antibiotic use after experiencing self-limiting respiratory tract infections (RTIs) may not be well-founded.

A new technological approach to genome editing that can clear latent and productive herpesvirus infections from human cells in vitro could eventually lead to a potent prophylactic.
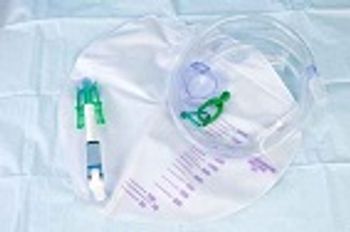
Both inappropriate catheter use and rates of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be reduced in the non-intensive care unit (ICU) setting.

A new bacteriophage (phage) treatment-based approach to fighting Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) colonization and infection may one day provide for effective treatment against this potentially lethal disease.

This review article provides guidance for clinicians that have been struggling with the most effective way to treat chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in children and adolescents.

A recent review focuses on the biology of human papillomaviruses, their associated burdens, and the clinical data available on HPV vaccine efficacy.
A long-held belief regarding the way in which vaccinations work to protect hosts from pathogens may be inaccurate.
A recent review article on the status of vaccines in development for healthcare associated infections (HAIs) provides both an in-depth discussion of their urgent need, as well as their potential for success.

A recent report describing the development of “flesh-eating bacteria” in a Louisiana woman has the public concerned. The infection developed after the woman injured her foot, resulting in bleeding, while surf fishing in the Gulf of Mexico earlier this May.
Management of visceral leishmaniasis poses a daunting challenge, in part due to the side effects associated with the use of the traditional treatment. However, one vaccine development strategy has recently shown promising results.

Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) can be spread between facilities, particularly in older adults. One study has found that collaboration between facilities may help curb the spread of this potentially deadly infection.

Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) can have dramatic effects on excess morbidity and associated costs and so finding effective and efficient way to prevent them is important.

A program designed to improve the quality of influenza surveillance capabilities in 39 countries from around the globe through partnership with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) seems to have resulted in remarkable progress on all six of the assessed metrics, and even led to improvements in the surveillance of other pathogens, according to the results of a recent study.

The level of hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) used as the traditional gold standard for evaluating influenza vaccines in the United States and European Union may not actually be the best predictor of protection from influenza virus-induced disease.
Researchers from the department of pathology at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston developed and validated a high-throughput screen (HTS) that could detect antimicrobial agents with the ability to restore carbapenem susceptibility to resistant strains, as well as those that target CRE directly.

The consequences of not understanding the actual rate of asymptomatic influenza infection can be grave, as influenza virus infection of the respiratory tract has been shown to result in severe disease and complications, including pneumonia, shock, renal failure, encephalopathy, and multiorgan dysfunction, which can be lethal.
Older antibiotic agents show decreased potency due to overuse and the subsequent emergence of drug-resistant bacteria. This antimicrobial resistance has been predicted to have enormous consequences for human health, necessitating the development of new agents in the ongoing war between humans and the germs that attack us.
The results of a methylome-wide analysis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) chronically infected, combination anti-retroviral therapy (cART)-treated individuals recently published in Molecular Cell suggest that HIV+ individuals have an epigenetic age 4.9 years older than healthy controls, resulting in an expected total mortality risk increase of 19%.

It is hoped that this proof of concept research may lead to promising new drug candidates to combat hPIV-3, which is the principal cause of acute respiratory illness in infants.
A recent review article on the status of influenza vaccines, their short-comings, and ways to improve them suggests the potential for significant improvements in the performance of future influenza vaccines.
Because certain viral sub-types are associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality than others, efforts to improve the effectiveness of influenza vaccines remain an important focus of future research.




































