
We are adding 2 more reasons to the 7 reasons we are more at risk than ever for a global pandemic.

We are adding 2 more reasons to the 7 reasons we are more at risk than ever for a global pandemic.
In a recent study, scientists from the NIH identify a set of protein complexes that are recruited viral genes and stimulate not only initial HSV infection, but also reactivation of dormant HSV.
More comprehensive molecular and genetic sequencing could help link cases to each other and alert authorities to HIV “clusters” that otherwise might be missed.
Manufacturing issues have led to a shortage of the only yellow fever vaccine licensed in the United States; now, that shortage is expected to lead to a complete depletion of available vaccine by mid-2017.
In underserved nations where HIV rates are high, rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) have been relied upon to determine which individuals are infected; however, there is concern about the accuracy of these tests.

The University of Iowa experienced a large mumps outbreak last year, despite almost 100% adherence to 2-dose measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine schedule, which begs the question, is it time to start recommending a 3-dose schedule?

Using a model implemented in Europe in 2013 to estimate HAI prevalence by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), Nicola Thompson, PhD, CDC, and her team estimated the national burden of HAIs in US nursing homes. In their poster, Dr. Thompson and her colleagues reported preliminary data from their pilot study.
The CDC offers insight into why a rare exception to the general recommendation of either brand of MenB vaccine had been made for the Rutgers outbreak in 2016.

While widespread and regional flu continue to decline in the United States, a new study examines how flu vaccine effectiveness and uptake can be improved.

Do some healthcare-associated infections receive more attention at your institution than others? Has your institution committed to using single-use medical devices to stave off infections? The editorial staff at Contagion® wants your feedback. Please take this brief survey to weigh-in.

This week’s Public Health News Watch shifts the focus towards pop culture as a Grammy award winner, and one of the foremost activists for the HIV/AIDS crisis has been taken ill with what news outlets are reporting as a “rare and potentially deadly bacterial infection.”
Despite initial attempts by WHO to eradicate yaws from Asia, several island nations in Asia continue to report active cases of the disease in humans.
Two studies published in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Emerging Infectious Diseases journal have outlined just how local and travel-related Zika cases differ, as well as which testing method is most sensitive to Zika virus RNA.
In populations with high presumptive immunity to measles, the infection can still spread when there is intense contact between patients or high levels of exposure.

The New England Journal of Medicine recently published two pieces on yellow fever. The first reports on the situation in the Americas, while the second recounts the case of a man from Angola who was found to be coinfected with yellow fever and Japanese encephalitis virus, although he reported no history of travel.

On World Malaria Day, the world focuses on how to eliminate malaria once and for all.

Contagion® recently spoke with Carissa Holmes, MPH, CDC, who discussed how policy change can work to strengthen infection prevention practices.
Study results presented today at the 2017 66th Annual EIS Conference provided the first statistical evidence for herd protection from the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
Adriano de Bernardi Schneider, MS, PhD Candidate, Contagion® Editorial Advisory Board Member, provides a brief snapshot into some of his work on mapping the evolution of the Zika virus.

Using statistical mapping strategies, UCLA researchers have found that the WHO and UNAIDS strategy to eliminate HIV in sub-Saharan Africa is not feasible because it doesn’t consider several important factors.

In case you missed them, here are our top 5 articles for the week of April 16, 2017.
The World Health Organization just published the first ever Global Hepatitis Report, which notes that the viral hepatitis mortality rate is increasing worldwide, while deaths caused by HIV and tuberculosis continues to drop.
An outbreak of MRSA at a Los Angeles-area hospital’s neonatal intensive care unit has raised questions about when health officials were notified of the outbreak, and why the public was not informed sooner.

A recent study finds that children who are infected with HIV either just before or after birth are at much greater risk of experiencing serious health events—and even death—than children who are infected during adolescence.

Topline results of a recent phase 3 clinical trial have shown that iclaprim is as effective as vancomycin for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs).
A new study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has shown American Indians in the Four Corners region of the United States are disproportionately affected by the hantavirus.
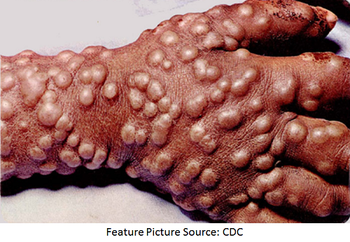
Although the eradication of smallpox was declared by the World Health Assembly in 1980, the deadly disease might make a comeback. The question is, will we be prepared for it?

A new report from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reveals information on a 5-month-old male infant who was diagnosed with the emerging tick-borne virus in Connecticut in 2016.

Liver health education seems to be absent from the final draft of the National Academy of Science's Strategy for Eliminating Viral Hepatitis B & C.
The FoodNet report in the CDC’s most recent MMWR provides insight on food-borne illnesses in 2016.