
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes measures necessary to confront invasive fungal infections from the pathogens posing highest threat and greatest disease burden.
Ken reports on medical innovations and advances in practice and edits presentations for news and professional education publications. He previously taught and mentored pharmacy and medical students, and provided and managed pharmacy care and drug information services. He regularly contributes to Contagion Live, Patient Care Online and Pain Medicine News.

The World Health Organization (WHO) describes measures necessary to confront invasive fungal infections from the pathogens posing highest threat and greatest disease burden.

The World Health Organization's fungal priority pathogens list is intended to prompt research, development and policy against the increasing health threat.

Polio outbreak has CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices considering a novel oral vaccine 20 years after shelving its predecessor.

CRISPR edit of proviral DNA tested as potential cure for HIV in first participant of phase 1/2 clinical trial.
Novel β-lactamase inhibitor enmetazobactam with cefepime exceeded noninferiority to piperacillin/tazobactam in complicated UTI, pyelonephritis.
Oral antibiotics after partial completion of intravenous regimen for S aureus bacteremia improves outcomes of persons who inject drugs (PWID), which is a population that often has limited access to treatment.

Largest extended study of outcomes after rare myocarditis from mRNA COVID-19 vaccines finds most recover and regain quality of life.
Occult HBV infection is likely to go undetected in under-resourced regions of high HBV endemicity and confound WHO goal to eradicate the viral hepatitis by 2030.

Progress in rapid diagnostic and point-of-care testing propelled by the pandemic can improve timeliness and precision of anti-infective treatment.
The same 5-year survival rates with kidney transplants from HCV positive and negative donors supports revising HCV "penalty" in ranking donors.

"Real-world" population study finds the oral antivirals authorized for non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients can benefit when started in the hospital.

Reviewers weigh evidence for the benefit of oral PrEP protection from HIV with risk of exacerbating hepatitis B.

Oral antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir is shown to be effective treatment for seniors against Omicron.
The young adult contracting paralytic polio in Rockland County, New York in June is the first since the WHO declared the Americas polio-free in 1994.

WHO guidelines on HIV, hepatitis and STIs focus on populations with high risk of infections but low inclusion in prevention and treatment programs.

WHO issues new HCV treatment recommendations that include "radical simplification" of care pathways, in pursuit of testing and treatment goals.

CDC links 2021 outbreak of tuberculosis in US affecting 113 persons and causing at least 3 deaths to bone grafts from one infected, deceased donor.

Next generation antimalarial monoclonal antibody is three times more potent than predecessor in preventing parasitemia, stopping parasite replicating.

Finding that the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted best antibiotic practices, the CDC announced further efforts to curb treatment-resistant infections.

Implicating adenovirus for hepatitis of unknown cause in children is confounded by its absence in some cases, and from all tested hepatic tissue.

CDC attributes a 15% increase in deaths from antimicrobial-resistant infections in 2020 to impacts of COVID-19 on health and healthcare.

Work group from infectious disease associations proposes prioritizing 6 areas of research to improve efficacy and precision of antibiotic therapy
Investigational vaccine demonstrates efficacy against respiratory syncytial virus in trial with adults inoculated with active RSV.

Algorithm offers guidance on clinically managing pregnant individuals exposed to monkeypox and on treating the virus during pregnancy.

Carbapenem-resistant enterobacterales in Saudi Arabia were genotyped and the course of illness characterized to help inform treatment and prevention.

At separate press conferences, the CDC and WHO indicate that containing monkeypox will depend on testing, tracing, and currently available vaccines.

The first report from WHO Scientific Advisory Group for the Origins of Novel Pathogens (SAGO) concedes SARS-CoV-2 source remains a mystery.

Rebound in COVID-19 symptoms, retesting positive for SARS-CoV-2, and recurring infectivity after Paxlovid treatment mars "test and treat."
New vaccine for COVID-19 employing receptor-binding domain-dimer-based platform achieves 87.6% efficacy against severe to critical illness.
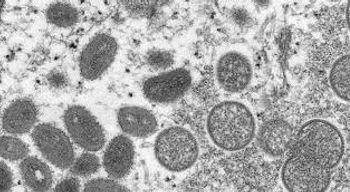
Community transmission of monkeypox outside traditional endemic regions of the virus prompts calls for increased vigilance.